A review of the Supernote Nomad after three months
For all my life I've enjoyed writing notes by hand. I liked taking notes in school, and I like taking notes at work. It helps me remember what we talk about, and gives me a reference point when coming back to something after a break.
However, I have a collection of literally hundreds of notebooks in my attic. I have every notebook I've written since university, and a few from high school.
I don't know exactly why I keep them. I only ever revisit them for two reasons. When I'm updating my resume I sometimes review them to remember what I was doing in a particular year. And occasionally I like to pull out a piece of music that I wrote years ago and dust it off on the piano.
But I don't like waste.
And I was struggling with another issue, too: I was too addicted to streaming services. My Galaxy tablet made it too easy to watch Netflix, and the reading experience was terrible.
So when I heard about the Supernote Nomad, I decided to take the plunge. At this point I've owned it for around three months, and I want to share my thoughts about it with the internet.
Features of the Supernote Nomad
I was drawn to the Supernote Nomad for a few specific reasons.
- Size. It's about the size of the small notebooks that I prefer to use. It's small enough that I can easily carry it in one hand with my laptop while I have a coffee in my other hand.
- Doodling. The Supernote tablets are among a number of recent tablets that allow the user to write notes out by hand. They also allow me to doodle in the margins, which is my favorite activity in long, boring meetings.
- Export. The Supernote Nomad offers the ability to export not only to pdf, but also to image formats. Weirdly I couldn't find this feature on the Amazon Kindle Scribe.
The good, the bad, and the ugly
After using it for a few months, I can verify that my reasons for choosing it were justified. The drawing and note-taking experience is generally very similar to writing with a pen. The tablet allows me to export to image formats and share them to Dropbox very easily. And the size is nicely compact as well.
But the size isn't quite perfect. I like to write on lined paper, and the smallest lines offered by the system only allow for 17 lines of text to be written on one page. So I could fit much more text on one page if the lines were just a little closer together.
The battery life is great. Like similar e-ink tablets, the battery lasts long enough that I forget to charge it. I typically charge once a week.
The reading experience is also great. It's very similar to the old Kindle e-ink tablets that I loved reading on before Amazon introduced the Kindle Fire, and generally spoiled the experience by trying to do too many things.
One thing that I don't like so much is that the display does that e-ink thing where it needs to be refreshed every few pages. The prior pages sort of remain lightly on the screen in the background, and this can build up and become distracting until you swipe to refresh the screen.

Another small nitpick is that the pen sometimes seems to write when it isn't touching the screen. This requires the user to re-calibrate the pen, which is easy enough, but sort of annoying.
And my final complaint is that the carrying case is entirely necessary. The device shouldn't be sold without it. I first bought it alone and figured that I would get a third party case, but this makes the experience of turning it off and on rather awkward. The normal way to turn it off and on is to use magnets in the first party case. This essentially makes it function like any other notebook. So if you're considering buying one, just know that you should factor in the cost of the first party case.
Otherwise I'm very happy with it. I'm not going to give it a numerical score, but I will simply say that I'm glad I decided to purchase it.
I like slow tech
The thing I like most about the Supernote Nomad is that the design pushes me into things I want to do with tech, rather than the things that exist to give me cheap hits of dopamine. The Supernote Nomad basically allows me to read a book, take notes, or do some sketching. There's no streaming services or videogames. There's no web browser or social media. There's no text messaging.
It's slow tech that is designed for humans.
The Supernote Nomad is a human friendly device in a way that standard tablets just aren't.
I hope that larger tech companies take notice of the Supernote tablets. I want to see more devices that work at human speed rather than as fast as possible. I want to see more devices that feel comfortable and well designed.
So if you're looking for a piece of tech that feels like it isn't forcing you to be constantly connected and constantly consuming, then I encourage you to consider it.
Are dynamic accumulators a garden myth?
I was listening to episode 444 of the excellent Joe Gardener Show when the guest brought up so-called dynamic accumulators. She mentioned them in the context of permaculture, and repeated the conventional wisdom about using tap rooted plants such as comfrey to pull nutrients up from deep in the soil.
The guest was Brandy Hall from Shades of Green Permaculture. Here's what she said.
Dynamic accumulation. That's a term that's really popular in permaculture. Deep taprooted plants that pull nutrients up, assuming the nutrients are in the soil. You know they aren't pulling them from thin air. Pulling what's there up into their leaves. Those leaves die in the winter and then those nutrients are released into the upper horizons of the soil.
It's hard for me to hear about dynamic accumulators from experts because to me, dynamic accumulators seem like the gardening equivalent of bigfoot. They are much talked about, but when you try to examine them, they disappear.
The concept of dynamic accumulators feels a little thin to me, so in this blog post I'm going to try to pin them down and see what sticks.
Defining dynamic accumulators is hard
The big problem with dynamic accumulators is that they have no scientific definition. Some people say that they are plants that pull nutrients from the soil and store them in the leaves. Other people tie the concept to tap roots. They say that dynamic accumulators pull nutrients from deep in the soil and bring them to the surface.
Unfortunately, these ideas are both flawed to my understanding.
All plants pull nutrients from the soil and move them into their bodies. That's basically the definition of a plant. Plants use sunlight to combine water with nutrients in the soil to make sugars and other nutrients that they store in their bodies and give away in the soil food web. Every single plant does this, so the concept is meaningless as a distinction.
And the idea that tap roots pull nutrients up from deep in the soil doesn't make much sense to me either. The vast majority of nutrients in the soil are in the top few layers of soil. The nutrients are in the organic matter in the humus and the topsoil.
It makes no evolutionary sense for a plant to send a deep tap root into the soil with the fewest nutrients. It would be much better off sending fibrous roots into the top few layers of soil.
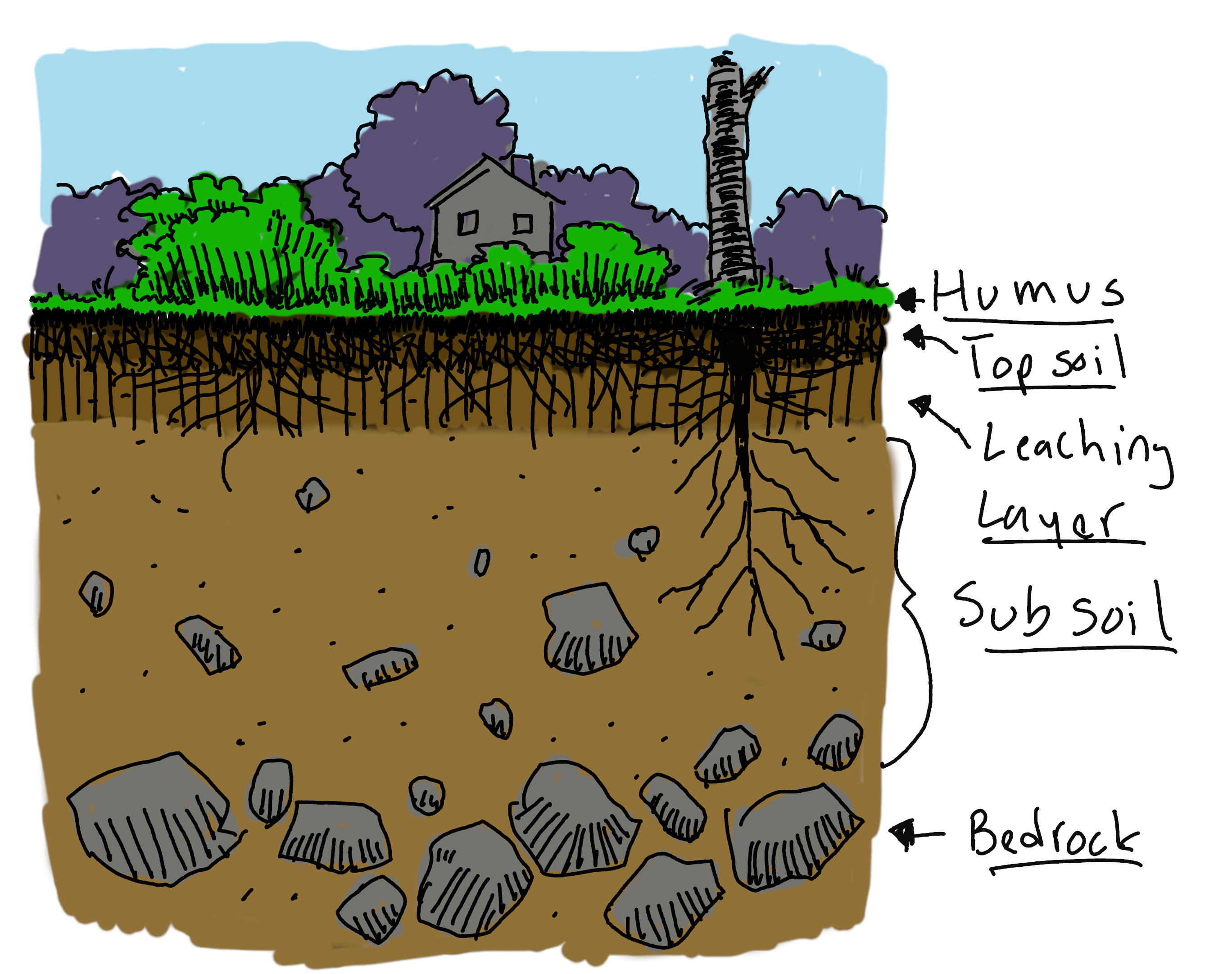
So if dynamic accumulators don't stand up to my own critical thinking, how are they being discussed by professionals and scientists?
What does science say about dynamic accumulators?
The best overview of the topic of dynamic accumulators that I've found is Breaking Ground with Dynamic Accumulators by Greta Zarro. She points out that practically everything we think we know about dynamic accumulators is indeed anecdotal. It's not based on evidence.
But she also points out that this is beginning to change in some interesting ways.
For instance, there's an effort to pin down a scientific definition of what qualifies as a dynamic accumulator in reference to existing classifications of plants that remove specific things from soil.
While dynamic accumulators are used to gather beneficial nutrients from the soil, hyperaccumulators are used to gather toxic heavy metals. When used for soil remediation, the plant tissue of hyperaccumulators is harvested and removed from the site. To qualify as a hyperaccumulator, a plant must accumulate metals above established threshold concentrations: 100ppm (for Cd), 1,000ppm (for Co, Cu, Ni, As, and Se), and 10,000ppm (for Zn and Mn). Brown suggests that similar thresholds should be set for dynamic accumulators, in ppm, using dried plant tissue samples, consistent with hyperaccumulator thresholds.
She points to work by Brown and Kourik that goes even further.
Kourik suggested that dynamic accumulators should demonstrate high amounts of nutrient accumulation, as compared to other plants. To address this, we started by setting the thresholds at 200% of nutrient value averages, which results in about 10.40% of plants qualifying in each nutrient category. However, for this model to endure, the thresholds need to be fixed at specific values rather than remain relative to the averages, because those averages will change over time as new plants are added to the databases. So we rounded off the thresholds and set them at even numbers, still roughly 200% of the averages, representing the top 10.08% of plants.
And since that article is from 2020, we can now look at the results of the author's two year study of dynamic accumulators.
Unfortunately, the results aren't quite clear. While it's true that some of the plants they studied were indeed able to accumulate higher concentrations of some nutrients, these levels were almost always in proportion to what was already in the soil. It was very rare that plants were able to accumulate high levels of specific nutrients in poor soil.
Perhaps most importantly, we found that plant tissue nutrient concentrations are relative to soil nutrient concentrations. Dynamic accumulators are well-suited to extract specific nutrients from fertile soil, but they aren’t going to create nutrition that isn’t there...That said, even when grown in poor, unamended soil, two species surpassed dynamic accumulator thresholds. Dried lambsquarters foliage was found to possess potassium concentrations that exceeded dynamic accumulator thresholds (40,715 ppm), and liquid fertilizer made by steeping lambsquarters foliage in water for 5 days contained the highest potassium concentrations of all the trial crops (903 ppm)... Likewise, Russian comfrey foliage surpassed dynamic accumulator threshold concentrations for both potassium (52,959 ppm) and silicon (513 ppm), with similarly high potassium concentrations found in the resulting liquid fertilizer (889 ppm).
They also found that stinging nettle made particularly good fertilizer, both in a liquid form, and when chopped and dropped directly onto the soil.
We found stinging nettle foliage to possess the highest calcium concentration of all trial crops... Liquid fertilizer derived from stinging nettle foliage proved to be very nutrient rich, possessing the highest concentrations of P, B, Ca, Cu, and Mn after 5 days of steeping compared to all other trial crops, as well as the highest nutrient carryover rates for all of these nutrients plus K and Mg, meaning stinging nettle’s nutrients are particularly soluble and well suited for liquid fertilizer.
The results with stinging nettle were consistent with the idea that dynamic accumulators are pulling nutrients up from the subsoil.
Chopping and dropping with stinging nettle also produced some exciting results. Calcium concentrations more than doubled in the 0-6” and 6-12” soil horizons, while dropping to 63% in the 12-24” soil horizon. This is consistent with the widely held belief that dynamic accumulators enrich the topsoil by extracting nutrients from the subsoil.
Dynamic accumulators sound a lot like...
But science isn't driven by one study or one scientist. Science builds a picture of the truth by combining the work of many scientists and many different experiments. While these initial experiments show some interesting results that seem to lend credence to some of what permaculturists have been saying for years, the studies are far from conclusive.
And what does this work even say?
It says that dynamic accumulators are plants that are particularly good at absorbing some specific nutrients from the soil, and if you chop and drop those plants then you can increase the amount of those nutrients available in your top soil.
So the question I want to leave you with is this: How are dynamic accumulators any different from cover crops? How is chopping and dropping comfrey or stinging nettle much different from chopping and dropping buckwheat or some other cover crop? The particular selection of nutrients may be different, but otherwise it seems pretty similar.
In the beginning of this post, I said that dynamic accumulators were a garden myth because when you examine them, they seem to disappear. That seems to have occurred again here. We looked at the latest study on dynamic accumulators, and the findings of that study essentially say that dynamic accumulators are the same thing as cover crops.
I'll leave it up to you to decide whether you want to cling to the concept of dynamic accumulators as used in the permaculture literature. For me, dynamic accumulators still seem like little more than a buzz word.
Three underappreciated jazz Christmas albums
There is an overwhelming amount of great Christmas music out there. We're spoiled for choice. Yet, we tend to hear the same Christmas music over and over again. The radio stations, grocery stores, and spotify playlists all collaborated to ensure that we only hear selections from a handful of classic albums.
And I love some of those albums. I love to hear Michael Buble, Tony Bennett, Louis Armstrong, Ella Fitzgerald, and even Mariah Carey at Christmas time.
But I also love the other stuff. I love the Christmas music that was once popular, but has fallen out of favor. I love Christmas music that's a little bit weird, but also kind of wonderful.
Here are three of my favorite jazz Christmas albums that you haven't heard a million times in the grocery store.

A Big Band Christmas
This is a compilation of big band Christmas music that was released in 1988. I particularly like it because it's full of great big band arrangements of tunes that have become standards. Virtually every song on here is a classic, but the version in this compilation isn't the one you've heard a million times. I love the version of Winter Weather on this album.
Crescent City Christmas Card
There was a time in the 1990s when the name Wynton Marsalis was synonymous with new jazz. He was everywhere, and you couldn't avoid his music if you wanted to. At the time I was pretty tired of his music.
Since then the world has cooled on him a bit, and I only recently discovered this Christmas album that he recorded in 1989. He puts a unique spin on every tune on the album.
Consummation
Okay, I don't even know if this last one is even a Christmas album. It's by Thad Jones and Mel Lewis, and every track on it is brilliant.
But the recording of A Child is Born is the best recording of the tune. So even if that's the only "Christmas" song on it, it's a great Christmas album. You could have a great night just by putting that one track on repeat.
How to use GitHub Actions to build and deploy an 11ty website
I love GitHub Actions. It is my favorite platform for continuous integration and deployment by far. It takes most of the concepts from tools like Jenkins and TeamCity, and packages them into a tight, easy to use framework.
Plus, GitHub Actions has a wonderful free plan. So I use GitHub for hosting the repository for my blog, and I use a simple GitHub Actions script to build and deploy it to AWS.
In this article, I'm not going to show you how to set up AWS to host your static site. I'm just going to give you a basic overview of the setup that I use, and give you the simple example script that I use to build and deploy my blog.
Requirements
This is the simplest and cheapest way that I've found to host a static website on AWS. There are definitely cheaper blog platforms out there, but this way gives you full control over every aspect your site, and leaves you the flexibility to evolve your site in the future.
Here are the prerequisites for using this deploy script on GitHub Actions.
- An 11ty website
- A GitHub repository that contains your website
- An AWS S3 bucket that is configured to host publicly available files
- An AWS cloudfront distribution that serves as a cache for the content on S3
- AWS access credentials that can update the S3 bucket and CloudFront distribution that have been saved into secrets on your GitHub repository called AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY.
The CloudFront distribution is necessary for caching, and for applying an SSL certificate to your site so that you can safely use the secure https protocol.
You need to set up each of those things before you can use this script.
Modifying the example script
First you should copy this code into a file that is saved into ".github/workflows/main.yaml", where the ".github" folder is in the root directory of your repository.
Then you will then need to modify the example script below in several ways.
If you're using a static site generator other than 11ty, then you need to modify the part of the example script where it says "Build the website". That script will depend on the framework you are using.
Where it says "<YOUR_S3_BUCKET>", you will need to replace that with the name of your S3 bucket.
You will also need to replace "<YOUR_FOLDER_TO_IGNORE>" in the section "Upload files to s3 with AWS CLI" if there are any files in your S3 bucket that the script shouldn't delete. I have folders for images and documents that I want to stay in the same place no matter what is in the repository. So that part of the script ensures that those folders aren't touched.
Finally, you will need to replace "<YOUR_CLOUDFRONT_DISTRIBUTION_ID>" with the string ID of your actual CloudFront distribution.
Then all you will need to do is push that script to your master branch on github. It should handle the rest.
Example script to deploy an 11ty static site to AWS S3 using GitHub Actions
name: Build and push to s3
on: [push]
jobs:
build_deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@master
- name: Build the website
run: npx @11ty/eleventy
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: us-west-1
- name: Upload files to s3 with AWS CLI
run: aws s3 sync _site/ s3://<YOUR_S3_BUCKET> --delete --exclude "images/*" --exclude "<YOUR_FOLDER_TO_IGNORE>"
# Invalidate Cloudfront. Based on https://community.ops.io/jei/deploy-a-web-app-to-s3-with-cloudfront-invalidation-via-github-actions-4433
- name: Issue Cloudfront invalidation
uses: chetan/invalidate-cloudfront-action@master
env:
DISTRIBUTION: '<YOUR_CLOUDFRONT_DISTRIBUTION_ID>'
PATHS: '/*'
AWS_REGION: 'us-west-1'
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
For more, see these blog posts:
Impermanence is a virtue: Why building for forever is folly
When I first started gardening, I was jealous of all the beautiful gardens I saw on social media. On Instagram I saw so many beautiful gardens filled with gorgeous raised beds. Or the gardeners were building these amazing structures for growing their annual vegetables. So, of course, I wanted the same thing for my garden.
I ordered fancy metal raised beds by whatever company was being advertised by the social media gardeners. You know the ones I'm talking about. They're about three two and a half feet tall and they look like they're made from corrugated tin. When they arrived, I assembled them and placed them in my yard, and filled them with some pretty expensive soil.
In fact, I dotted my entire backyard with raised beds. Some of them I purchased online, but others I built for myself from lumber I got at the hardware store. I put raised beds on my lawn, on my patio, and on all the ugly concrete that was laid by the last owner of my home. I was reclaiming that space for garden vegetables!
But there was still some leftover space in my backyard. There were a few spots of neglected, in-ground soil where I decided that I could plant a few seeds directly in the soil.
Then I watched my plants grow, and I was surprised by what happened. The raised beds required much more water than the plants in the ground. In fact, they required thorough watering on every hot day of the summer. The ones on hot concrete required even more water, and I indignantly watched a lot of it filtering out the bottom and into the drain!
In fact, the seeds in the soil germinated more quickly, required less care, and produced far, far more fruit.
Getting the moisture and the soil right in a tall raised bed turned out to be very difficult.
So the following year I decided to change things up. I took apart the raised beds that I'd built from lumber, and I turned them into shallow raised beds directly on the soil. A shallow, 6 inch deep raised bed has some of the advantages of a raised bed along with some of the advantages of planting directly in the ground.
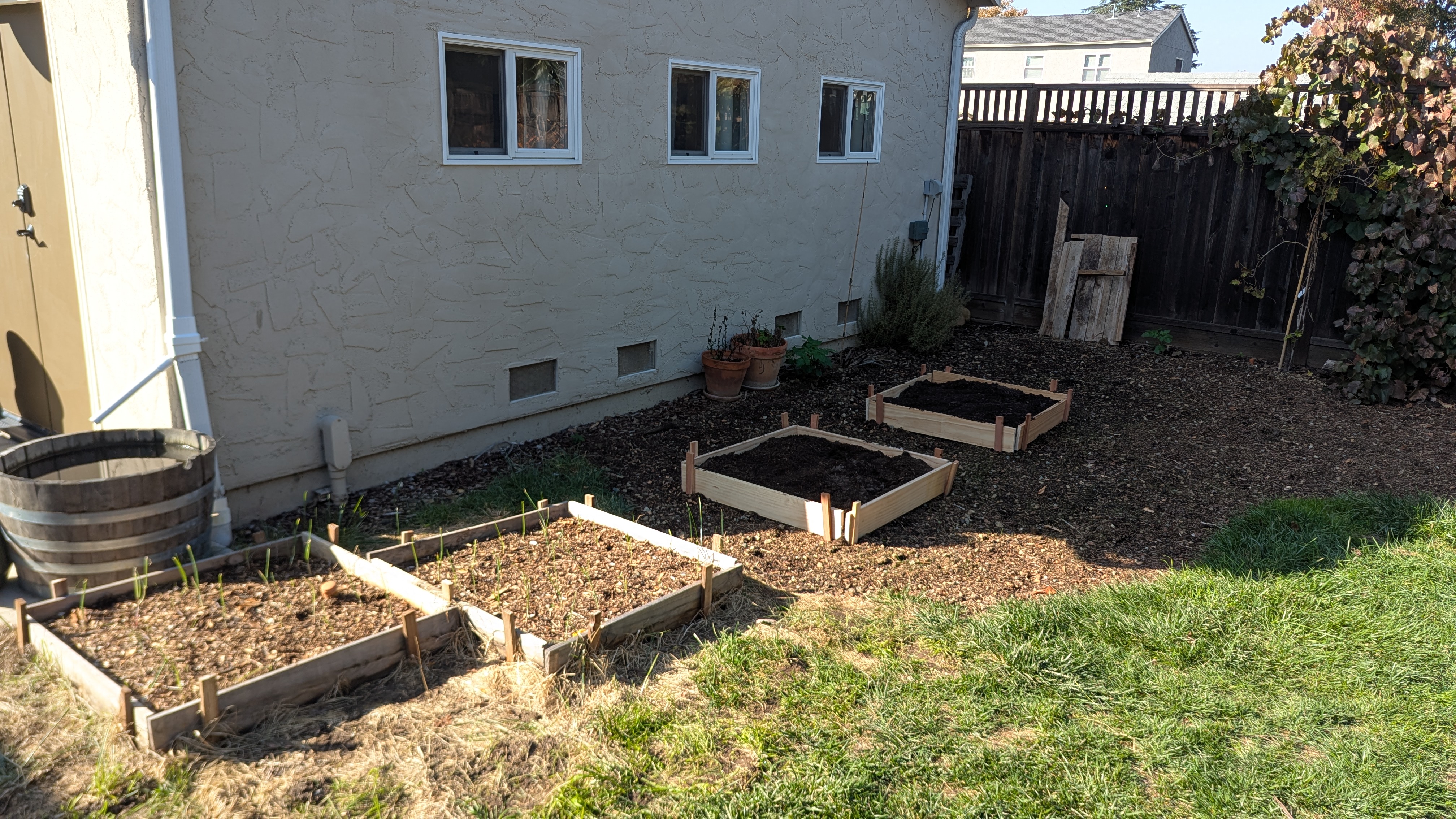

That turned out to be the most successful planting method that I've yet discovered. A shallow raised bed directly on the ground is easy to care for, easy to maintain, and easy to build. It's affordable, too. It requires less lumber, and less soil. It costs a fraction of what the fancy metal beds cost, and it even costs less than tall homemade beds.
Unfortunately, I was then stuck with all the "fancy" raised beds I'd purchased online. They looked more like expensive trash than the key to backyard success.
Buying those metal raised beds was a mistake.

And unfortunately, so much of my yard was taken up by a patio that I didn't have room for a bunch of shallow raised beds directly on the soil.
I knew that in order to install more shallow raised beds, the patio would have to come out, even though it wasn't very old. The previous owner had only put it in to sell the place around six years ago.
Building the patio had also been a mistake.
I know now that building for "permanence" is absurd. Especially in the garden. It's nothing but hubris to think that the thing you're building this year will last forever.
It won't.
And not only that, but you won't even want it to last forever. In a year or two or three, you will start to see the flaws in the thing you built. Maybe you'll see that you put it in a suboptimal place, or that it isn't quite right for what you planned to use it for. Or maybe you'll just tire of whatever motivated you to build it in the first place.
You WILL change. You WILL move on. You WILL see things differently.
Which is why I now build beds that I can easily disassemble, move, and reuse. I build garden beds simply by cutting lumber into one meter square sections, and tacking them into the ground using wooden stakes.
These beds cost next to nothing, they are the BEST way to grow annual vegetables, and they can be easily disassembled and moved every time I decide to do something different.
The thinking that we need to build something to last can be a trap. It's what leads people to build shopping malls that sit empty after shopping trends move on. It's what leads people to build from materials that will be used for a few years at most, then will idle in a landfill for eternity.
Don't get me wrong, the idea of single use items isn't great either.
But there is a middle ground.
Building for impermanence is a virtue because it's an extension of using only what you need.
So build that cheap garden bed out of biodegradable materials. When you inevitably regret it, or want to change it next year, it will be that much easier to do so.
