Discovering artist Viola M. Allen
I recently purchased Emerging from the Shadows, Vol. I: A Survey of Women Artists Working in California, 1860-1960 and while reading it I discovered one particularly interesting artist named Viola M. Allen. Her facility with a palette knife seems almost miraculous, so of course I started searching the web for more of her work. Other than a few items available at auction, I haven't been able to find much information. So I wanted to share a couple quotes from the fabulous book by Maurine St. Gaudens.
Viola M. Allen was born on March 14, 1906, in Queens, New York, the daughter of Safarine D. Allen and Minnie (Eschman) Allen. According to her biographical artist's promotional card, she attended, in New York, the Pratt Institute and the National Academy of Design, where she studied under Charles Curran. Her card also indicates that she studied portrait painting with Moskowitz and Borgdonav and sculpture with Haffner and Monahan. A resident of Manhattan, New York, through the 1930s, by the latter part of the decade she had moved to Los Angeles, California; she remained a California resident until her death.

A study of Viola's paintings shows that she was a palette knife painter. Her ability to create realistic compositions by applying oil paint to a canvas, or board, by the use of a flexible painter's palette knife rather than a brush is found in most of her work; it is a difficult technique and one not widely practiced. Palette knives vary in length and width, and each one has a different tip, enabling the artist to achieve a different type of stroke, with the oil painting usually being applied very thickly on the canvas or board. During her career Viola had a commercial art studio in Malibu for many years where she did illustration and advertising art. In California, she exhibited with the California Art Club, 1955-1967.
This was all I could find out about her, and I'm happy to share it on the internet, and hopefully bring a little more attention to an artist who clearly had a control over the palette knife that few have ever achieved.
Of course I had to see if I could find one of her works at a reasonable price, and ebay came to my aid once again. I was able to find this beautiful small landscape listed for a song and now it hangs over my desk next to Sam Hyde Harris and Quincy Tahoma.
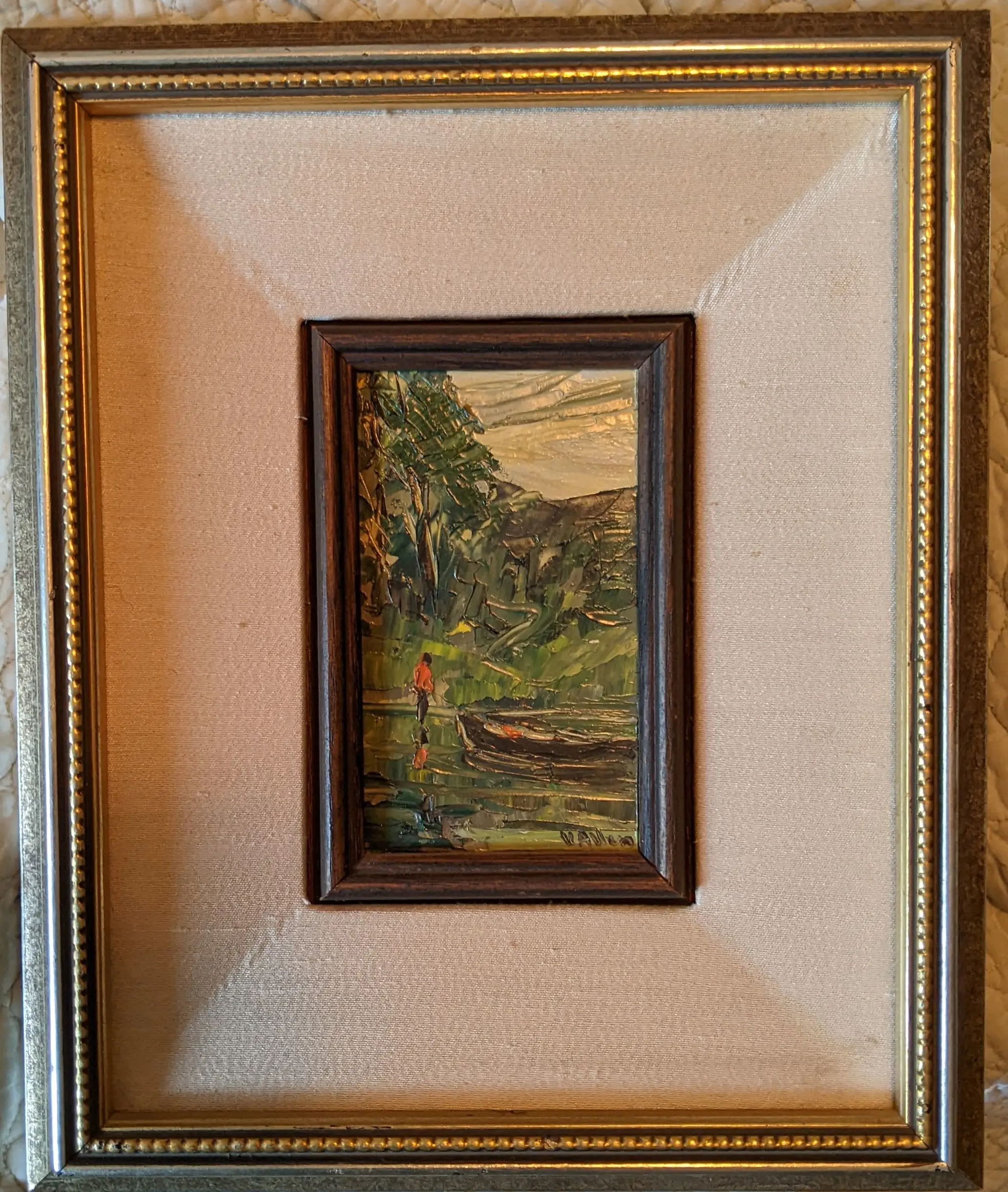
I don't think I've ever seen another artist wield a palette knife as fluently as she did, so I'll be on the lookout for more of her work. I hope that the internet can help preserve the legacy of a great artist who clearly deserves a re-evaluation.
Why to stick with Heroku, or make the switch
One question I hear a lot lately is when a company should stick with Heroku or switch to something else. In this article I'm going to lay out the pros and cons for Heroku, and compare it with the typical alternative, AWS.
Three reasons to stick with Heroku
Don't fall victim to thinking that "the grass is always greener on the other side." That hot new technology on AWS or Azure may look cool now, but Heroku offers a lot of great features that should fit the bill for many growing companies.
Heroku supports easy scaling with sticky sessions
Horizontally scaling any web application is hard. In a traditional web app, you must optimize your code so that it runs in parallel. You must deal with race conditions that arise when multiple servers are trying to interact with a shared resource such as a cache or a database. You must find a way to balance load across multiple servers while sharing state across all instances.
Session data is visitor-specific data that is stored on the server. If a visitors's session is stored on one server, but their request is routed to another server, then that server won't know about anything they've done in the current session. It may not know if they're logged in or not. It may not have the browsing filters that they've configured.
Session affinity, also known as sticky sessions, is one solution to the problem of sharing session across servers. With session affinity enabled, all of a visitor's requests will always be routed to the same instance. There are some drawbacks to session affinity, but the benefit of being able to scale horizontally before having to tackle some parallelization problems may outweigh the drawbacks in your use case.
Many services offer session affinity, but none are as easy to set up as Heroku. With literally two clicks you can enable session affinity and start scaling out. Don't let hype distract you from an approach that may reap benefits for your web property.
Heroku provides zero down time deploys and upgrades
One of the best features of Heroku is that their technology and support teams handle deploys and upgrades. They make it so that your dev team doesn't have to worry about keeping the servers up during deploys or running migrations during upgrades.
The preboot feature allows you to keep the old version of your app running during a deploy. This means that users will only ever be routed to a server that has booted up and is running your app, and that means that you aren't turning away customers in that 30 second window where the new version of your app is loading.
Heroku also supports seamless upgrades for the most popular add-ons, such as REDIS. When I switched my company from Heroku REDIS to AWS REDIS we were surprised that our site went down a few weeks after the switch. AWS may force upgrade your technology without providing a way to seamlessly switch to the new version. So AWS forces you to track each upcoming patch and ensure that your team is ready for the switch.
Heroku is cheaper than the alternative because anyone can use it
Heroku seems very expensive when the bills come due, but in my experience it's cheaper than the alternative. Heroku is so easy to use that anyone can use it. With a few clicks or commands a backend developer can enable sticky sessions. With a few clicks or commands they can enable preboot. With a few clicks or commands they can add REDIS or PostGreSQL or any of the many add-ons provided by Heroku.
To use all those different products on a less managed product, such as AWS or Azure, you must retain a dedicated DevOps specialist. These people have very specialized skills and are not cheap. In my experience, using Heroku saves the cost of around one expensive employee. So as long as your Heroku bill is less than the cost of one employee, it's probably the more affordable option.
Three reasons to switch
There are many good reasons to stick with Heroku, but it certainly has limits. Here are the reasons why I've moved services from Heroku to somewhere else in the past.
Heroku is dangerous because anyone can use it
When you're on Heroku, you may not need to hire dedicated staff to manage your web infrastructure. This is a significant cost savings, but it means that the DevOps tasks are going to be offloaded on your web programmers. So you must ensure that you hire the skills on your team to understand Heroku. Heroku may not be as complex as AWS, but it still requires a foundational understanding of how the web works, linux, and logging. If your programmers are exploring the features in Heroku without the requisite experience or training then they may make mistakes that harm your business.
Heroku offers fewer options for international support
Heroku lacks flexible support for internationalized websites. As it says in the regions documentation, each "Private Space exists in a single region, and all applications in the Private Space run in that region.". This may sound confusing, but it ultimately means that each project in Heroku can only run in one region. If you want to support another region, then it must be in a separate project and hosted at a separate domain or subdomain. So if you want to internationalize your website using subdirectories, which is advantageous because it inherits the existing search reputation of your domain, then you can't do that with geographically distributed servers on Heroku.
Heroku offers fewer vertical scaling options
Heroku dynos come in six different flavors as of this writing. If you need anything outside of those six options then you are out of luck. The beefiest dyno is the performance-l machine, which offers 14Gb of RAM. If you need more than that, then you need to switch to another platform. What if you're using very little memory, but you want to use many CPU cores? The only option is to pay for the most expensive dynos. This lack of flexibility means that if your web service is a pretty standard website or API, then Heroku probably won't serve your needs very well.
How to decide whether to stick with Heroku or to switch
In this article I've listed some reasons to stick with Heroku and some reasons to switch, but the final decision is largely dependent on your use case. If you are making a pretty standard website or API, then Heroku is probably fine even when horizontally scaling. There are three main scenarios where you should strongly consider switching to a more complex cloud hosting service.
- Your service need more flexible options for internationalization
- Your service doesn't match the requirements common to most web apps and APIs
- Your service is scaling exponentially
Evan's React Interview Cheat Sheet (for 2022)
In this article I'm going to list some of the things that are useful in React coding interviews, but are easily forgotten or overlooked. Most of the techniques here are useful for solving problems that often arise in coding interviews.
Table of contents
- Imitating componentDidMount using hooks
- Using the previous state in the useState hook
- Using useRef to refer to an element
- Custom usePrevious hook to simplify a common useRef use case
- Vanilla js debounce method
- Use useContext to avoid prop-drilling
Imitating componentDidMount using React hooks
The useEffect hook is one of the more popular additions to the React hooks API. The problem with it is that it replaces a handful of critical lifecycle methods that were much easier to understand.
It's much easier to understand the meaning of "componentDidMount" than "useEffect({}, [])", especially when useEffect replaces componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate, and componentWillUnmount.
The most common use of the useEffect hook in interviews is to replace componentDidMount. The componentDidMount method is often used for loading whatever data is needed by the component. In fact, the reason it's called useEffect is because you are using a side effect.
The default behavior of useEffect is to run after ever render, but it can also be run conditionally using a second argument that triggers the effect when it changes.
In this example, we use the useEffect hook to load data from the omdb api.
// fetch movies. Notice the use of async
const fetchMovies = (newSearchTerm = searchTerm) => {
// See http://www.omdbapi.com/
fetch(`http://www.omdbapi.com/?apikey=${apikey}&s=${newSearchTerm}&page=${pageNumber}`).then(async (response) => {
const responseJson = await response.json();
// if this is a new search term, then replace the movies
if(newSearchTerm != previousSearchTerm) {
setMovies(responseJson.Search);
} else {
// if the search term is the same, then append the new page to the end of movies
setMovies([...movies, ...responseJson.Search]);
}
}).catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
});
};
// imitate componentDidMount
useEffect(fetchMovies, []);
Note that this syntax for using asynchronous code in useEffect is the suggested way to do so.
Using the previous state in the useState hook
The useState hook is probably the easiest and most natural hook, but it does obscure one common use case. For instance, do you know how to use the previous state in the useState hook?
It turns out that you can pass a function into the useState set method and that function can take the previous state as an argument.
Here's a simple counter example.
const [count, setCount] = useState({});
setCount(prevState => {
return prevState + 1;
});
Using useRef to refer to an element
The useRef hook is used to store any mutable value across calls to the component render method. The most common use is to use it to access an element in the DOM.
Initialize the reference using the useRef hook.
// use useRef hook to keep track of a specific element
const movieContainerRef = useRef();
Then attach it to an element in the render return.
<div className={MovieListStyles.movieContainer} ref={movieContainerRef}>
{movies && movies.length > 0 &&
movies.map(MovieItem)
}
</div>
Then you can use the .current property to access the current DOM element for that div, and attach listeners or do anything else you need to do with a div.
// set up a scroll handler
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = debounce(() => {
const scrollTop = movieContainerRef.current.scrollTop;
const scrollHeight = movieContainerRef.current.scrollHeight;
// do something with the scrolling properties here...
}, 150);
// add the handler to the movie container
movieContainerRef.current.addEventListener("scroll", handleScroll, { passive: true });
// remove the handler from the movie container
return () => movieContainerRef.current.removeEventListener("scroll", handleScroll);
}, []);
Custom usePrevious hook to simplify a common useRef use case
The useRef hook can be used to store any mutable value. So it's a great choice when you want to look at the previous value in a state variable. Unfortunately, the logic to do so is somewhat tortuous and can get repetitive. I prefer to use a custom usePrevious hook from usehooks.com.
import {useEffect, useRef} from 'react';
// See https://usehooks.com/usePrevious/
function usePrevious(value) {
// The ref object is a generic container whose current property is mutable ...
// ... and can hold any value, similar to an instance property on a class
const ref = useRef();
// Store current value in ref
useEffect(() => {
ref.current = value;
}, [value]); // Only re-run if value changes
// Return previous value (happens before update in useEffect above)
return ref.current;
}
export default usePrevious;
Using it is as simple as one extra line when setting up a functional component.
// use the useState hook to store the search term
const [searchTerm, setSearchTerm] = useState('orange');
// use custom usePrevious hook
const previousSearchTerm = usePrevious(searchTerm);
Vanilla js debounce method
Okay, this next one has nothing to do with React, except for the fact that it's a commonly needed helper method. Yes, I'm talking about "debounce". If you want to reduce the jittery quality of a user interface, but you still want to respond to actions by the user, then it's important to throttle the rate of events your code responds to. Debounce is the name of a method for doing this from the lodash library.
The debounce method waits a preset interval until after the last call to debounce to call a callback method. Effectively, it waits until it stops receiving events to call the callback. This is commonly needed when responding to scroll or mouse events.
The problem is that you don't want to install lodash in a coding interview just to use one method. So here's a vanilla javascript debounce method from Josh Comeau.
//
const debounce = (callback, wait) => {
let timeoutId = null;
return (...args) => {
window.clearTimeout(timeoutId);
timeoutId = window.setTimeout(() => {
callback.apply(null, args);
}, wait);
};
}
export default debounce;
Here's an example of how to use it to update a movie list when a new search term is entered.
// handle text input
const handleSearchChange = debounce((event) => {
setSearchTerm(event.target.value);
fetchMovies(event.target.value);
}, 150);
return (
<div className={MovieListStyles.movieList}>
<h2>Movie List</h2>
<div className={MovieListStyles.searchTermContainer}>
<label>
Search:
<input type="text" defaultValue={searchTerm} onChange={handleSearchChange} />
</label>
</div>
<div
className={MovieListStyles.movieContainer}
ref={movieContainerRef}
>
{movies && movies.length > 0 &&
movies.map(MovieItem)
}
</div>
</div>
);
Use useContext to avoid prop-drilling
The last thing an interviewer wants to see during a React coding interview is prop drilling. Prop drilling occurs when you need to pass a piece of data from one parent component, through several intervening components, to a child component. Prop drilling results in a bunch of repeated code where we are piping a variable through many unrelated components.
To avoid prop drilling, you should use the useContext hook.
The useContext hook is a React implementation of the provider pattern. The provider pattern is a way of providing system wide access to some resource.
It takes three code changes to implement the useContext hook. You've got to call createContext in the parent component that will maintain the data. Then you've got to wrap your app with a special tag.
export const DataContext = React.createContext()
function App() {
const data = { ... }
return (
<div>
<DataContext.Provider value={data}>
<SideBar />
<Content />
</DataContext.Provider>
</div>
)
}
Then you've got to import the context in the child component, and call useContext to get the current value.
import DataContext from '../app.js';
...
const { data } = React.useContext(DataContext);
What has made you stumble in React interviews?
What are some other common ways to make mistakes in React coding interviews? Send me your biggest React coding headaches on Twitter @EvanXMerz.
How to measure the performance of a webpage
Measuring the performance of a webpage is an extremely complex topic that could fill a book. In this article I'm going to introduce some of the commonly used tools for measuring web performance, and show you why you need to take multiple approaches to get a complete picture of the performance of any webpage.
Why measure webpage performance?
Why measure webpage performance? Performance is so critical to the modern web that this question seems almost comical. Here are just a few reasons why you should be measuring and monitoring webpage performance.
- User experience impacts Google search rankings via Core Web Vitals.
- Page load time correlates with conversion rate and inversely correlates with bounce rate.
- Pages must be performant to be accessible to the widest possible audience.
Four approaches to measuring performance
No single tool is going to give you a comprehensive perspective on webpage performance. You must combine multiple approaches to really understand how a page performs. You must look at multiple browsing patterns, multuple devices, multiple times of day, and multiple locations.
In this article, I'm going to talk about four different approaches to measuring the performance of a page and recommend some tools for each of them. You must use at least one from each category to get a complete picture of the performance of a webpage.
The four approaches I'm going to talk about are...
- One time assessments
- Live monitoring and alerts
- Full stack observability
- Subjective user tests
Why do we need multiple perspectives to measure performance?
People who are new to monitoring web performance often make mistakes when assessing web performance. They pull up a website on their phone, count off seconds in their head, then angrily email the developers complaining that the website takes 10 seconds to load.
The actual performance experienced by users of your website is an important perspective, but there are dozens of things that can impact the performance of a single page load. Maybe the page wasn't in the page cache. Maybe the site was in the middle of a deploy. Maybe hackers are attacking network infrastructure. Maybe local weather is impacting an ISP's network infrastructure.
You can't generalize from a single page load to the performance of that page. I've seen many people fall into this trap, from executives to marketing team members. It makes everyone look bad. The website looks bad because of the slow page load. The developers look bad because of the poor user experience. The person who called it out looks bad because it looks like they don't know what they are doing. The data analysts look bad because they aren't exposing visualizations of performance that other team members can use.
So read this article and fire up some of the tools before sending out that angry email.
Please note that the tools listed here are just the tools that I have found to be effective in my career. There are many other options that may be omitted simply because I've never used them.
One time assessments
One time assessments are the most commonly used tools. One time assessments can be run against a production webpage at any time to get a perspective of the performance at that moment. One thing that's nice about these tools is that they can be used effectively without paying anything.
PROS:
- Easy to use
- Easy to quantify
- Fast
- Reliable
- Affordable
CONS:
- May lack perspective over time
- Lacks perspective on actual browsing patterns, including subsequent page loads
- Lacks perspective on other locations
- May lack information on the source of an issue
TOOLS:
Live monitoring and alerts
The performance of a webpage can degrade very quickly. It can degrade due to poor network conditions, an influx of bot visitors from a new ad, a influx of legitimate visitors during peak hours, or from the deploy of a non-performant feature.
When the performance does degrade, you need to know immediately, so you can either roll back the deploy, or investigate the other factors that may be slowing down the site.
Notice that price isn't listed as a benefit (pro) or drawback (con) of live monitoring tools. You generally need to pay something to use these tools effectively, but usually that price is less than $100 a month, even on large sites.
PROS:
- Real-time notifications of performance changes
- Easy to quantify
- Can be configured to request from other locations
CONS:
- Limited information
- Lacks perspective over time
- May lack information on the source of an issue
- Fragile configuration can lead to false positives
TOOLS:
Full stack observability
Some tools offer insights into the full page lifecycle over time. These tools are constantly ingesting data from your website and compiling that data into configurable visualizations. They look at page load data on the client side and server side using highly granular measurements such as database transaction time, and the number of http requests.
If you wanted a single source of information to measure performance on your site, then these tools are the only option. They can provide one time assessments, monitoring, and backend insights.
One big problem with these tools is that they are quite complex. To use these tools effectively, you need developers to help set them up, and you need data analysts to extract the important information exposed by these tools.
PROS:
- Includes detailed breakdowns that can help identify the source of performance issues
- Includes data over time
- Highly granular data
CONS:
- Difficult to use
- Expensive
- Requires developer setup and configuration
TOOLS:
Qualitative user tests
The final approach for measuring the performance of a webpage is subjective. In other words, you must actually look at how your site performs when real people are using it. This can be as simple as opening a website on all your devices and trying to browse like a normal user, or you can set up time to interview real users and gather qualitative information about their experience.
I once worked at a company that required developers to attend in-person user tests every two weeks. This allowed every developer to see how users actually browsed and experienced their work. This may be overkill for most companies, but it's a perspective that can't be ignored.
PROS:
- No additional tools are necessary
- Exposes actual, real world user experience
- Exposes issues raised from real browsing patterns including subsequent page loads
CONS:
- It's easy to prematurely generalize from a small number of cases
- Can be expensive and difficult to do well
- Difficult to quantify
- Not timely
TOOLS:
- Web browsers on multiple devices
- Google Analytics
- User testing services
Conclusion
In this article, I introduced four different ways to measure the performance of a webpage. Each of them is necessary to get a full understanding of the performance of a page. I also introduced some of my favorite tools that can be used for each approach.
The four approaches are...
- One time assessments
- Live monitoring and alerts
- Full stack observability
- Subjective user tests
I hope that this prepares you to start wading into the complex world of measuring website performance.
How to optimize largest contentful paint (LCP) on client side
In this article I'm going to show you some strategies I've used to optimize websites on the client side for largest contentful paint (lcp) and first contentful paint (fcp).
What is largest contentful paint and why does it matter?
Largest contentful paint (LCP) is a measure of how long from initial request it takes for your site to render the largest thing on screen. Usually it measures the time it takes your largest image to appear on screen.
First contentful paint (FCP) is a measure of how long from initial request it takes for your site to render anything on screen. In most cases, optimizing LCP will also optimize FCP, so this is the last time I'll mention FCP in this article.
Google Core Web Vitals considers 2.5 seconds on mobile to be a good LCP when loading the site at 4g speeds. This is an extremely high bar to reach, and most sites won't come close without addressing it directly.
It's also important to note that reaching an LCP of 2.5 seconds once is not sufficient to pass. Your pages must achieve an average LCP of under 2.5 seconds over a period of 28 days in order to pass. This means that putting off work on LCP will only be more painful in the future. You need to act now to move your LCP in the right direction.
Why not use server side rendering?
When searching for ways to optimize LCP, I came across various sites that suggested server side rendering. They suggest that rendering the page server side and delivering it fully rendered client side would be the fastest. I know from experience that this is wrong for several reasons.
First, you still need to render on client side even if you deliver a flat html/js/css page. The client side still needs to extract and compile the page, and that takes the bulk of rendering time for modern, js-heavy webpages.
Second, rendering server side can only possibly be faster if your site isn't scaling. Yes, when you have a small number of simultaneous users, it's much faster to render on your server than on an old android. Once you hit hundreds or thousands of simultaneous users that math quickly flips, and it's much faster to render on thousands of client machines, no matter how old they are.
Why not use service workers?
Another suggestion I see is to use service workers to preload content. Please keep in mind that Google only measures the first load of a page. It does not measure subsequent loads. So any technique that improves subsequent loads is irrelevant to Google Core Web Vitals. Yes, this is incredibly frustrating, because frameworks like Next.js give you preloading out of the box.
Optimize images using modern web formats and a CDN
The most important thing you can do to achieve a lower LCP is to optimize the delivery of your images. Unless you use very few images, as I do on this blog, then images are the largest part of the payload for your webpages. They are typically around 10 to 100 times larger than all other assets combined. So optimizing your images should be your number one concern.
First, you need to be using modern web image formats. This means using lightweight formats such as webp, rather than heavier formats such as png.
Second, you need to deliver images from a content distribution network (CDN). Delivering images from edge locations near your users is an absolute must.
Third, you need to show images properly scaled for a user's device. This means requesting images at the specific resolution that will be displayed for a user, rather than loading a larger image and scaling it down with css.
Finally, Google seems to prefer progressive images, which give the user an image experience such as a blurred image before the full image has loaded into memory. There are many robust packages on the web for delivering progressive images.
I suggest you consider ImgIX for optimizing your images. ImgIX is both an image processor and a CDN. With open source components that work with various CMSs, and in various environments, ImgIX is a one stop shop that will quickly solve your image delivery issues. I've used it at two scaling websites, and in both cases it has been extremely impactful.
Deliver the smallest amount of data to each page
After you optimize your images, the next thing to consider is how much data you are sending to the client. You need to send the smallest amount of data that is necessary to render the page. This is typically an issue on list pages.
If you're using out-of-the-box CRUD APIs built in Ruby on Rails, or many other frameworks, then you typically have one template for rendering one type of thing. You might have a product template that renders all the information needed about a product. Then that same product template is used on product detail pages, and on list pages. The problem with that is that much less information is needed on the list pages. So it's imperative that you split your templates into light and heavy templates, then differentiate which are used in which places.
This is more of a backend change than a frontend change, but optimizing frontend performance requires the cooperation of an entire team.
Deliver static assets using a CDN
After putting our images through ImgIX, we stopped worrying about CDNs. We thought that because images were so much larger than the static assets, it wouldn't make much difference to serve static assets from our servers rather than a CDN.
This is true, if you are just beginning to optimize your frontend performance. Putting static assets on a CDN won't lead to a tremendous drop in LCP.
However, once you are trying to get your page load time down to the absolute minimum, every little bit counts. We saved an average of around two tenths of a second on our pages when we put our static assets on a CDN, and two tenths of a second is not nothing.
Another great thing about putting your static assets on a CDN is that it typically requires no code changes. It's simply a matter of integrating the CDN into your continuous integration.
Eliminate third party javascript
Unfortunately, third party javascript libraries are frequently sources of a significant amount of load time. Some third party javascript is not minimized, some pulls more javascript from slow third party servers, and some uses old fashioned techniques such as document.write.
To continue optimizing our load time we had to audit the third party javascript loaded on each page. We made a list of what was loaded where, then went around to each department and asked how they were using each package.
We initially found 19 different trackers on our site. When we spoke with each department we found that 6 of them weren't even being used any more, and 2 more were only lightly used.
So we trimmed down to 11 third party javascript libraries then set that as a hard limit. From then on, whenever anyone asked to add a third party library, they had to suggest one they were willing to remove. This was a necessary step to meet the aggressive performance demands required by Google.
Optimize your bundle size
The final thing to do to optimize your client side load time is to optimize your bundle size. When we talk about bundle size, we're talking about the amount of static assets delivered on your pages. This includes javascript, html, css, and more. Typically, extracting and compiling javascript is what takes the bulk of the time, so that's what you should focus on.
Use code splitting
Code splitting means that your app generates multiple bundles that are potentially different for each page. This is necessary in order to deliver the smallest amount required for a given page. Most modern website transpilers like WebPack will do this automatically.
Forget import *
Stop using "import *" entirely. You should only ever import the methods you are using. When you "import *" you import every bit of code in that module as well as every bit of code that it relies on. In most circumstances, you only need a fraction of that.
It's true, that a feature called tree shaking is able to eliminate some of the cruft in scenarios where you're importing more than you need, but it's sometimes tough to figure out where the tree shaking is working and where it's failing. To do so, you need to run bundle analysis, and comb through it carefully.
It's much easier to simply stop using "import *".
Use composition wisely
I almost named this section "Forget the factory pattern", because the factory pattern creates situations very similar to "import *". In the factory pattern, a method is called that returns an object with all the methods needed to fulfill a responsibility or interface. What I see most often, is a misapplication of the factory pattern whereby programmers are dumping a whole bunch of methods into a pseudo-module then using only one or two methods.
// don't do this
const createDateHelpers = () => {
const formatDate = () => {...};
const dateToUtc = () => {...};
return {
formatDate,
dateToUtc,
}
}
You can see that if you want to call "formatDate", then you need to run "createDateHelpers().formatDate()". This is essentially the same as importing every method in the date helpers module, and again, you are importing all their dependencies as well.
This is where composition can be applied to make an object that gives you the full object when needed, but also allows you to export methods individually.
// use composition
export const formatDate = () => {...};
export const dateToUtc = () => {...};
export default const createDateHelpers = () => {
return {
formatDate,
dateToUtc,
}
};
Render a simplified static page
It's important to note that optimizing your existing pages isn't the only strategy available. Amazon's website crushes Google's Core Web Vitals, even though it isn't very fast. It does this by rendering a simplified static template for the first load, then filling it in with the correct content. So if you visit Amazon, you may see some evergreen content flash up on the page before content specific to you loads in.
That's a fine way to pass Google's Core Web Vitals, but it isn't optimizing the performance of your page. That's tailoring your page to meet a specific test. It's not cheating, but it's not necessarily honoring the intention of Google's UX metrics.
Conclusion
There are two basic categories of changes that are necessary to optimize the client side of a website for largest contentful paint: optimizing delivery of images, and optimizing delivery of code. In this article I've listed several strategies I've used in the past to address both of these categories. These strategies include using progressive images, using CDNs, and delivering as little data and code as is necessary to render a page.
